Austria's role in the unification of Germany is a complex and often overlooked aspect of European history. The country's strategic location and political influence played a significant part in the events leading up to the unification of the German states. Austria's involvement in the Napoleonic Wars and its subsequent alliance with Prussia against Napoleon Bonaparte set the stage for a potential alliance that could shape the future of Germany. This paragraph will explore the various ways in which Austria could have contributed to the unification process, considering its diplomatic relations, military capabilities, and cultural ties with the German states.
What You'll Learn
- Political Alliances: Austria's diplomatic efforts to form alliances with German states
- Economic Integration: Trade and economic policies fostering German-Austrian unity
- Cultural Exchange: Cultural and educational programs to bridge the Austrian-German divide
- Military Cooperation: Joint military strategies and alliances to unify Germany under Austrian leadership
- Historical Narratives: Shared historical narratives and monuments to promote German-Austrian unity

Political Alliances: Austria's diplomatic efforts to form alliances with German states
Austria's diplomatic strategy to unite Germany was a complex and multifaceted approach, heavily influenced by the country's unique position and historical context. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Austria was a dual monarchy, sharing power with Hungary, and faced significant challenges in its pursuit of German unification. The country's primary goal was to establish a strong alliance with the German states while navigating the complex political landscape of the time.
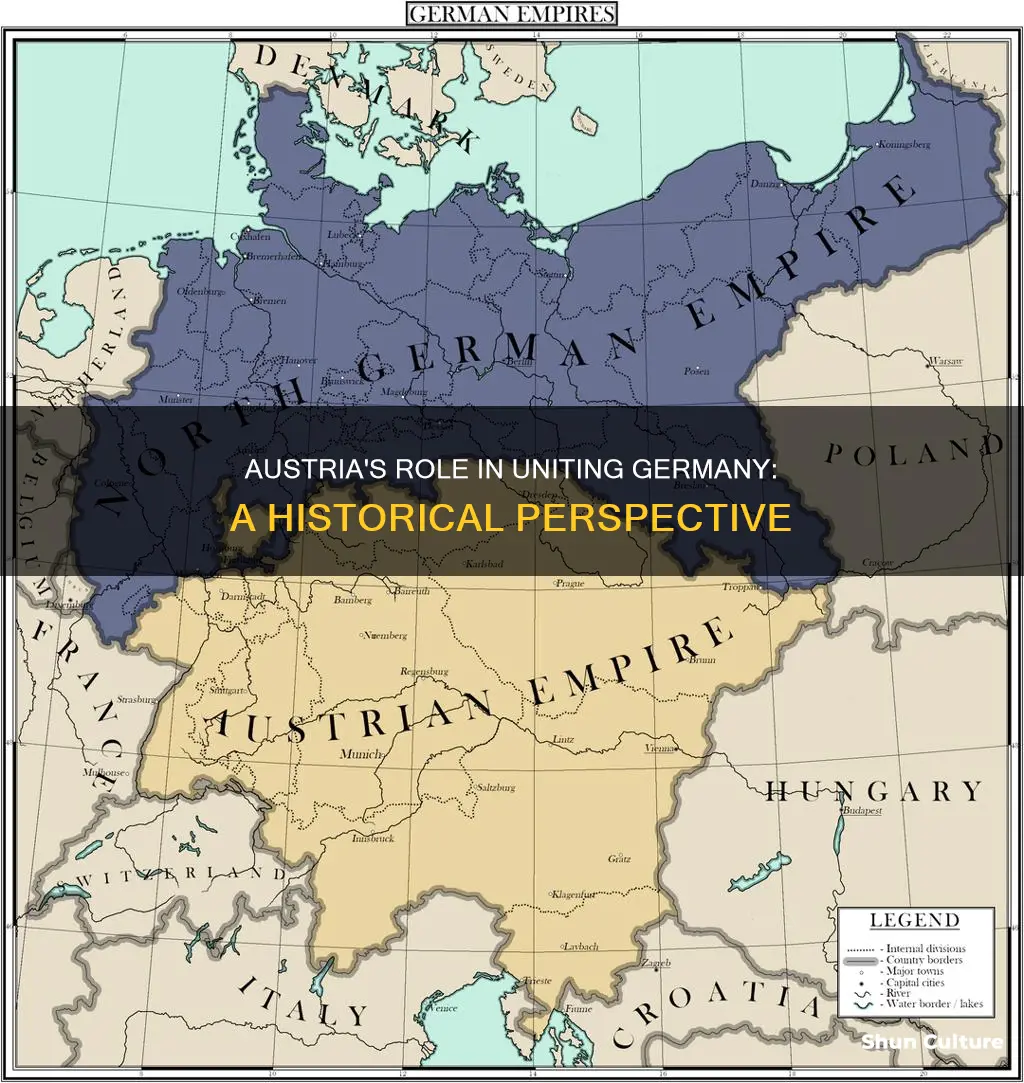
One of Austria's key diplomatic efforts was the formation of the German Confederation, a political alliance that aimed to unite the German states under a centralized government. This confederation, established in 1815, brought together various German states, including Prussia, Bavaria, and Austria, to promote economic and political cooperation. By fostering a sense of unity and shared interests, Austria sought to create a platform for further unification. The Confederation's primary objective was to counter the influence of Napoleonic France and to establish a stable and unified German political entity.
A significant milestone in Austria's diplomatic endeavors was the Austro-Prussian War of 1866. This conflict, fought between Austria and Prussia, had far-reaching consequences for the unification process. While Austria initially sought to maintain the status quo and preserve the German Confederation, Prussia's victory led to the establishment of the North German Confederation in 1867, excluding Austria and its allies. This event marked a turning point, as it highlighted the challenges of achieving unification through diplomatic means alone.
In response to the changing political landscape, Austria embarked on a series of diplomatic initiatives to re-establish its influence and promote German unification. The country actively engaged in negotiations and formed alliances with other German states, particularly those that shared similar political ideologies. One notable example is the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, which established a dual monarchy and granted Austria-Hungary a degree of autonomy within the multi-ethnic empire. This compromise aimed to balance the interests of various German-speaking regions while also fostering a sense of unity.
Furthermore, Austria's diplomatic efforts extended beyond the German-speaking world. The country sought alliances with other European powers to strengthen its position and gain support for German unification. Diplomatic missions and negotiations with Russia, Italy, and other European states were undertaken to build a network of alliances. These efforts aimed to create a favorable international environment and gain recognition for Austria's role in the unification process.
In summary, Austria's diplomatic efforts to form alliances with German states were driven by a desire to shape the unification process and secure its influence. Through the formation of the German Confederation, engagement in the Austro-Prussian War, and the establishment of the Austro-Hungarian Compromise, Austria sought to unite the German states while also addressing its own political and territorial ambitions. These political alliances played a crucial role in the complex journey towards German unification, leaving a lasting impact on the region's political landscape.
Traveling from Austria to Athens by Train: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

Economic Integration: Trade and economic policies fostering German-Austrian unity
The economic integration of Austria and Germany is a key aspect of fostering unity between the two countries. This integration can be achieved through various trade and economic policies that aim to strengthen their economic ties and create a more unified market. Here are some strategies to consider:
Trade Agreements and Tariff Reduction: Establishing comprehensive trade agreements between Austria and Germany can significantly boost economic unity. These agreements should focus on reducing or eliminating tariffs on goods and services, making cross-border trade more efficient and cost-effective. By harmonizing trade policies, the two countries can create a seamless border, encouraging the free flow of products and services. This reduction in trade barriers will not only increase the volume of trade but also enhance the competitiveness of businesses in both nations.
Economic Cooperation and Investment: Encouraging economic cooperation and investment between German and Austrian businesses can lead to a more integrated economy. This can be facilitated through joint ventures, mergers, and acquisitions, allowing companies to expand their operations across borders. Governments can provide incentives and support programs to promote cross-border investments, ensuring that businesses have the necessary resources to establish a strong presence in both markets. Additionally, fostering collaboration in research and development (R&D) can lead to technological advancements and innovation, benefiting industries in both countries.
Single Market Implementation: The concept of a unified single market, similar to the European Union's (EU) internal market, can be a powerful tool for economic integration. This involves aligning regulations, standards, and procedures to ensure the free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor. By adopting a unified approach to product regulations, labor market policies, and service provision, Austria and Germany can create a level playing field for businesses. This integration will enable companies to operate across borders without facing excessive regulatory hurdles, fostering a more competitive and integrated economy.
Infrastructure Development and Connectivity: Investing in transportation and communication infrastructure is essential for economic unity. Upgrading roads, railways, and digital networks will improve connectivity between the two countries, reducing travel and transportation costs. Efficient transportation networks will facilitate the movement of goods and people, making it easier for businesses to establish supply chains and distribution networks across the border. Additionally, high-speed internet and digital infrastructure will support the growth of e-commerce and digital services, creating new economic opportunities.
Financial Integration and Currency Stability: Achieving financial integration and ensuring currency stability are crucial for long-term economic unity. This involves coordinating monetary policies and fostering financial cooperation between the central banks of Austria and Germany. By working together, they can maintain a stable exchange rate, providing a more predictable environment for businesses and investors. Financial integration can also include the development of cross-border financial markets, allowing for easier access to capital and facilitating the management of economic risks.
Travel from Austria to Amsterdam: Train Options
You may want to see also

Cultural Exchange: Cultural and educational programs to bridge the Austrian-German divide
The concept of cultural exchange between Austria and Germany, aimed at bridging the historical and cultural divide, is a powerful approach to fostering unity and understanding. This initiative could take various forms, each designed to celebrate and explore the unique aspects of both nations while promoting mutual respect and appreciation. Here's a detailed plan for such a program:
Cultural Festivals and Events: Organize a series of cultural festivals in both countries, showcasing the arts, music, and traditions of each nation. These festivals can feature Austrian and German artists, musicians, and performers, providing a platform for them to share their heritage. For instance, a German music festival could highlight classical compositions by Austrian composers like Mozart and Beethoven, followed by contemporary German artists. Similarly, an Austrian festival might celebrate folk music and dance, showcasing the rich cultural heritage of the Alps. These events can attract tourists and locals alike, creating a shared experience and fostering cultural appreciation.
Educational Exchange Programs: Educational institutions in both countries can collaborate to offer exchange programs for students and scholars. These programs could provide an immersive experience, allowing participants to study, live, and interact with peers from the other country. For instance, German students could spend a semester in an Austrian university, taking courses in Austrian history, literature, and culture, while also engaging in language exchange. Similarly, Austrian students could benefit from studying in German universities, gaining insights into German philosophy, science, and the arts. Such programs would not only enhance language skills but also promote cross-cultural understanding and friendship.
Art and Literature Exhibitions: Curating joint art and literature exhibitions can be a powerful way to showcase the creative expressions of both nations. Austrian and German artists can collaborate on projects, creating a dialogue between the two cultures. For example, a photography exhibition could feature the work of Austrian and German photographers, each capturing the landscapes and people of their respective countries. Similarly, literature festivals could host readings and discussions by authors from both countries, exploring themes of unity, diversity, and shared experiences. These exhibitions and events can attract art enthusiasts and literature lovers, providing a platform for cultural dialogue.
Language Learning Initiatives: Language barriers can often be a significant hurdle in cross-cultural understanding. Therefore, initiating language learning programs can be highly beneficial. German and Austrian language schools or language exchange platforms can be established, encouraging mutual language learning. For instance, a language exchange program could pair German language learners with native Austrian speakers and vice versa, creating a supportive environment for language acquisition and cultural immersion. This initiative would not only improve language skills but also foster friendships and a deeper understanding of each other's cultures.
Historical and Cultural Research Projects: Encouraging historical and cultural research projects can provide a deeper understanding of the shared and unique aspects of both nations. Scholars and historians can collaborate on projects that explore the historical connections and influences between Austria and Germany. For example, a joint research project could examine the impact of the Holy Roman Empire on the formation of both nations, or the cultural exchange during the Renaissance period. These projects would not only contribute to academic knowledge but also promote a shared historical narrative, fostering a sense of unity and common heritage.
Vienna Airport: Is Vienna International Airport a Global Hub?
You may want to see also

Military Cooperation: Joint military strategies and alliances to unify Germany under Austrian leadership
The idea of Austria uniting Germany under its leadership is a complex and ambitious concept that would require significant military cooperation and strategic alliances. Here's an overview of how this hypothetical scenario could be approached:
Alliances and Diplomatic Efforts: Austria, with its rich history and military prowess, could initiate diplomatic missions to forge alliances with various German states. The goal would be to gain support for a unified Germany under Austrian rule. This process would involve extensive negotiations, treaties, and political maneuvering. Austria could propose a federal system where individual states retain a degree of autonomy while acknowledging Austrian leadership. This approach might appeal to states that value stability and a strong central authority.
Joint Military Commands: Establishing joint military commands and alliances would be a crucial aspect of this unification. Austria could propose the creation of a unified German army under Austrian command, with representatives from different states participating in decision-making. This structure would ensure that military strategies are coordinated across the region. Joint training exercises, combined arms operations, and the sharing of military resources could be organized to foster cooperation and interoperability between the various German states' armies.
Strategic Defense and Security: A unified German defense strategy would be essential to ensure security and stability. Austria could propose a comprehensive defense plan that addresses potential threats and outlines a unified military strategy. This might include the establishment of a collective defense pact, where member states agree to mutual protection and support in times of war or external aggression. By creating a unified front, Austria could ensure that Germany becomes a formidable military power, capable of defending itself and potentially influencing European politics.
Economic and Political Incentives: Military cooperation should be accompanied by economic and political incentives to encourage participation. Austria could offer favorable trade agreements, financial support, and political benefits to states that actively contribute to the unification process. This could include reduced tariffs, investment in infrastructure, and the establishment of a common market, which would benefit all participating states. Additionally, political concessions, such as the promise of representation in a unified German government, could further motivate states to join the alliance.
Regional Stability and Power Dynamics: Unifying Germany under Austrian leadership would significantly shift the power dynamics in Europe. Austria would need to carefully consider the potential reactions of neighboring powers and ensure that the unification process does not lead to regional instability. Balancing relations with other European states, especially those with historical ties to Germany, would be crucial. A well-executed military alliance could potentially deter external threats and create a more stable environment for the newly unified Germany.
Austria's Military Aid to Ukraine: Weapons and Beyond
You may want to see also

Historical Narratives: Shared historical narratives and monuments to promote German-Austrian unity
The concept of German-Austrian unity is deeply intertwined with shared historical narratives and the creation of monuments that commemorate significant events and figures from both nations' pasts. This approach aims to foster a sense of common identity and understanding between the two countries, which have a complex and often contentious history.
One of the key strategies to promote unity is the establishment of shared historical narratives that highlight the commonalities and interdependencies between Germany and Austria. This involves presenting a balanced and comprehensive account of historical events, focusing on the cultural, social, and political exchanges between the two regions. For instance, the narrative could emphasize the shared experiences of the Holy Roman Empire, the influence of the Hapsburg Empire, and the impact of the Napoleonic Wars on both territories. By doing so, the narrative provides a foundation for understanding the historical context that shaped the relationship between the two nations.
The creation of monuments and memorials is another powerful tool to encourage unity. These physical reminders of shared history can serve as educational resources and symbols of reconciliation. For example, the 'German-Austrian Peace Monument' in Vienna, unveiled in 1985, commemorates the end of the First World War and the subsequent peace treaty, which redrew the map of Europe. The monument, designed by Austrian artist Hans Bitterlich, features a large stone structure with a sculpture of a woman holding a dove, symbolizing peace and unity. Such monuments can become iconic landmarks, attracting visitors and serving as a constant reminder of the shared past and the importance of peace and cooperation.
Additionally, museums and cultural institutions play a vital role in promoting unity. These venues can showcase the rich cultural heritage of both nations, presenting artifacts, art, and exhibits that highlight the common threads and unique contributions of German and Austrian cultures. For instance, the 'German-Austrian Cultural Center' in Munich could organize exhibitions featuring the works of German and Austrian artists, writers, and musicians, providing a platform for cultural exchange and appreciation.
Furthermore, educational initiatives and programs can be designed to encourage the study and understanding of shared history. This could include joint history curricula in schools, where students from both countries learn about each other's historical experiences and perspectives. By fostering an early appreciation for shared narratives, these educational programs can contribute to long-term unity and understanding.
In summary, promoting German-Austrian unity through shared historical narratives and monuments is a multifaceted approach that aims to educate, inspire, and foster a sense of common identity. By presenting a balanced historical account and creating physical reminders of their shared past, the two nations can work towards a more harmonious and cooperative relationship, learning from their history to build a brighter future together.
Austria-Hungary's Entry into World War I Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Austria, as a powerful state in the German-speaking world, could have potentially influenced the unification process. While Austria was not directly involved in the political unification, it had significant cultural and linguistic ties with the German states. The Austrian Empire, with its capital in Vienna, had a strong presence in the region and could have provided a central authority or a cultural bridge to unify the diverse German-speaking territories.
One of the main challenges Austria faced was the conflict of interests between the German-speaking regions and the multi-ethnic Austrian Empire. Austria, with its diverse population, had to balance the needs and aspirations of various ethnic groups, which sometimes clashed with the goals of German unification. Additionally, the complex political landscape of the time, with competing powers like Prussia and the French Empire, made it difficult for Austria to take a decisive role in the unification process.
While Austria's direct political influence on the German states was limited, it did have some impact through cultural and diplomatic means. The Austrian Empire had a significant German-speaking population, and its cultural institutions and educational system contributed to the spread of German language and culture. Austria also engaged in diplomatic efforts to shape the unification process, often advocating for a federal structure that would have recognized its influence and interests.
One notable event is the Austro-Prussian War of 1866. This conflict between Austria and Prussia had significant consequences for the unification of Germany. Prussia's victory in the war led to the establishment of the North German Confederation, which excluded Austria and other Austrian-aligned states. This event created a rift between the German-speaking territories and influenced the direction of German unification, ultimately leading to the formation of the German Empire without Austria's direct involvement.







