Paris, Madrid, Angola, and Venezuela are not all north of Maine. Paris is in France, which is northeast of Maine. Madrid is in Spain, which is east of Maine. Angola is in southern Africa, and Venezuela is in South America, with both countries being southwest of Maine.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Location | Northern coast of South America |
| Population | 29 million (2022) |
| Capital | Caracas |
| Area | 916,445 km2 (353,841 sq mi) |
| Borders | Colombia, Brazil, Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana |
| -- | -- |
| Location | Northeastern United States |
| Population | 1,395,722 (2023) |
| Capital | Augusta |
| Area | 35,385 mi2 (91,646 km2) |
| Borders | New Hampshire, the Atlantic Ocean, New Brunswick, Quebec |
What You'll Learn
- Angola is a large country with a variety of landscapes, including a semi-desert Atlantic littoral, a rainforest interior, rugged highlands, and a densely populated northern coast
- Venezuela is a petrostate, where the government is highly dependent on fossil fuel income, power is concentrated, and corruption is widespread
- Paris, France, is at a higher latitude than Quebec or Maine
- Venezuela's oil exports have financed almost two-thirds of the government's budget
- Angola is bordered by Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo

Angola is a large country with a variety of landscapes, including a semi-desert Atlantic littoral, a rainforest interior, rugged highlands, and a densely populated northern coast
Angola is a large country with a variety of landscapes. Located on the west coast of Africa, it is washed by the Atlantic Ocean and bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, and Namibia. Angola's landscape includes a semi-desert Atlantic littoral, a rainforest interior, rugged highlands, and a densely populated northern coast.
The coastline of Angola stretches for over 1,600 km along the Atlantic Ocean, from the mouth of the Zaire River in the north to the Cunene River in the south. The northern coastline is characterised by gentle hills, while the area surrounding the capital, Luanda, is generally flat and uniform, with the estuaries of the Cuanza and Bengo Rivers. Further south, in the Benguela region, the mountains approach the Atlantic, and the landscape becomes a semi-desert, leading into the Namib Desert in the southwest corner of the country.
The interior of Angola is characterised by high plains covered in savannah, with the province of Cuanza-Norte being an exception, as it is covered in tropical rainforest. The largest of the Angolan highlands is the Bie Plateau, which occupies a significant portion of the country's territory and reaches an altitude of 1,300 meters. To the west of the Bie Plateau lie mountain ranges such as the Serra do Chilengue and the Serra do Humbe, which include the country's highest peak, Morro de Moco, at 2,620 meters.
Angola's northern coast is densely populated, with three of the country's most important cities located along the Atlantic coast: Luanda, Benguela, and Lobito. The country has a variety of ecosystems, including savannah, rainforest, and semi-desert, which support diverse wildlife and plant species.
Angola's varied landscapes offer significant natural attractions, such as the Calandula waterfalls on the Lucala River, the rocky area of Pungo Andongo, and the Namib Desert in the southwest. The country's diverse geography and ecosystems provide a home to a rich array of flora and fauna, making it a potential attraction for tourists once the necessary infrastructure is in place.
Angola, with its semi-desert Atlantic littoral, rainforest interior, rugged highlands, and densely populated northern coast, showcases a diverse range of landscapes and ecosystems, contributing to its status as a country with spectacular and unspoiled scenery.
Angola Rodeo: A Weekend of Wild West Action
You may want to see also

Venezuela is a petrostate, where the government is highly dependent on fossil fuel income, power is concentrated, and corruption is widespread
Venezuela is a petrostate, a country whose economy is heavily dependent on the extraction and export of oil or natural gas. Venezuela's government is highly dependent on fossil fuel income, with oil exports financing almost two-thirds of the government's budget in recent years. Venezuela has the world's largest oil reserves, and oil accounts for roughly a third of its GDP, around 80% of exports, and more than half of government revenues.
The oil industry represents 98% of the country's total exports, making Venezuela fiercely dependent on the international oil market. When Hugo Chavez came to power, crude oil production was around 3 million barrels per day. Since then, this has fallen to less than 1.3 million barrels per day due to poor management of the oil industry and widespread corruption.
Venezuela's economy is vulnerable to fluctuations in oil prices. When oil prices are high, the country tends to thrive, but it struggles when prices are low. The country's dependence on oil exports has led to a neglect of other sectors, such as agriculture and manufacturing, and has contributed to economic and political instability.
The discovery of oil in Venezuela in the 1920s marked the beginning of its transformation into a petrostate. Oil quickly came to dominate exports and government revenues, and the country became highly dependent on this natural resource.
The oil wealth has also contributed to economic and political concentration, with power resting in the hands of an elite minority. Venezuela has experienced democratic backsliding and a shift towards authoritarianism, with power concentrated in the executive branch and democratic institutions weakened. Corruption is widespread, and the country ranks low in international measurements of civil liberties and press freedom.
The oil wealth has also had social impacts, with Chavez using oil exports to finance unsustainable social programs and maintain social control. The fall in oil exports, combined with external debt and government spending, has led to hyperinflation and a severe economic crisis, causing shortages of basic goods, a decline in living standards, and a humanitarian crisis.
America's Most Brutal Prisons: A Terrifying Insight
You may want to see also

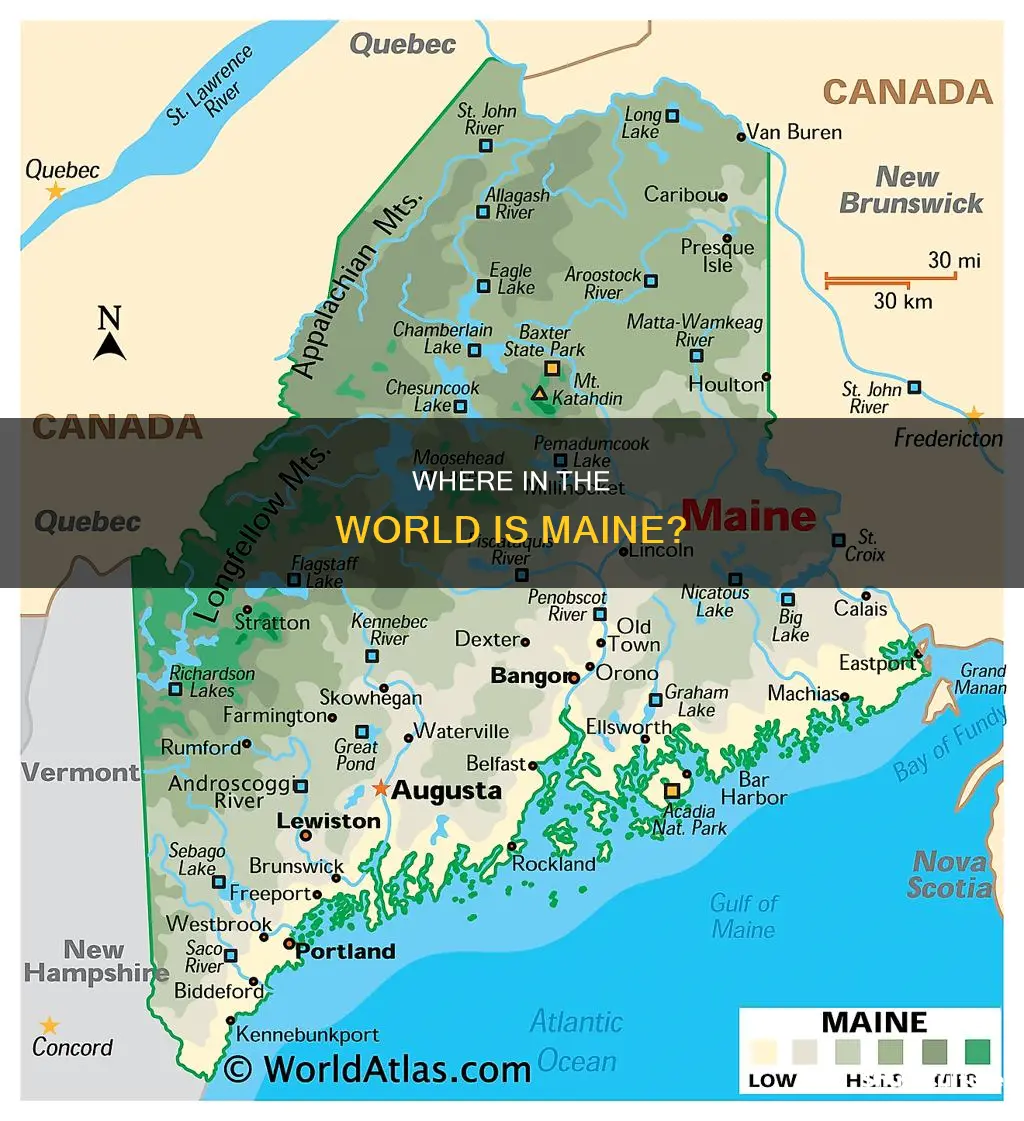
Paris, France, is at a higher latitude than Quebec or Maine
Paris, the capital city of France, is located in the north-central part of the country, in the region known as Île-de-France. Quebec City, on the other hand, is located in Canada and is the capital city of the province of Quebec. It is situated on the St. Lawrence River and is known for its beautiful architecture and rich cultural heritage. Maine, the northernmost state in the contiguous United States, is bordered by Canada to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
The latitudes of these three places reveal some interesting geographical relationships. Paris, despite being farther north than Quebec and Maine, has a relatively mild climate compared to these two locations. This is partly due to the influence of the Gulf Stream, which brings warm waters to Western Europe. Quebec, being farther north, experiences colder winters, and Maine, while sharing a similar latitude with Quebec, has a more temperate climate due to its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean.
The latitudes of Paris, Quebec, and Maine also influence the vegetation and ecosystems found in these regions. Paris, with its mild climate, supports a diverse range of plant life, including the famous Tuileries Garden and the Champs-Élysées. Quebec, with its colder winters, has vast forests and is known for its stunning fall foliage. Maine, influenced by its coastal location, has a mix of deciduous and coniferous forests, with pine, oak, and maple trees being common.
In addition to geographical differences, Paris, Quebec, and Maine each have their own unique cultural and historical significance. Paris is renowned for its fashion, art, and culinary traditions, with iconic landmarks such as the Eiffel Tower and Notre Dame Cathedral. Quebec City, with its French-speaking population, has a rich cultural heritage and is known for its historic Old Quebec, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Maine, known for its stunning natural scenery, also has a rich maritime history and is famous for its lobster cuisine and picturesque lighthouses along the rocky coastline.
Angola Incarceration: Exploring Sexuality Among Male Prisoners
You may want to see also

Venezuela's oil exports have financed almost two-thirds of the government's budget
Venezuela is a petrostate, meaning its government is highly dependent on fossil fuel income. In recent years, oil exports have financed almost two-thirds of the government's budget. Earnings from the state oil company PDVSA are expected to contribute $9.34 billion to the 2023 budget, a 14% increase on the previous year. Venezuela has the world's largest proven oil reserves, and oil exports account for around 95% of the country's exports.
Venezuela's economy has been in a state of collapse since 2013, with GDP falling by 80% in less than a decade. The country has been plagued by corruption, shortages, unemployment, mismanagement of the oil sector, and hyperinflation. Venezuela's oil production has declined due to years of divestment, mismanagement, and US sanctions. However, there is hope for a revival of the oil industry as the US has recently eased sanctions on Venezuela's oil and gas sector.
Angola Prison Caskets: Available for Purchase?
You may want to see also

Angola is bordered by Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north-east. Its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean. The country also has a small coastal exclave province called Cabinda, which borders the Republic of the Congo to the north and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south.
The Angola-Democratic Republic of the Congo border is 2,646 km (1,644 mi) long and consists of two non-contiguous sections. The first section, along the border with Cabinda, runs from the Atlantic Ocean to the tripoint with the Republic of the Congo. The second, much longer section runs from the Atlantic to the tripoint with Zambia.
Angola's neighbours have played a significant role in its history. The country's borders were established during the Scramble for Africa in the late 19th century, a period when European powers rushed to colonise the African continent. During Angola's anti-colonial struggle and subsequent civil war, its neighbours were often involved, with cross-border incursions and refugee flows.
Angola's borders enclose an area of 1,246,700 km2 (481,400 sq mi), making it the world's 22nd largest country. The country has a diverse geography, with a coastline that offers natural harbours, and an interior that features highlands, river valleys, and vast plains.
Angolan-Congolese Relations: A Historical Overview
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, only Paris and Madrid are north of Maine. Angola is a country in southwestern Africa, while Venezuela is a country on the northern coast of South America.
The capital of Angola is Luanda, which is also its commercial centre and a large port city.
Venezuela's official name is the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela.
Venezuela's population was estimated at 29 million in 2022.
Angola's population was estimated at 35,159,000 in 2024.







